Core Concept
The fundamental principle involves centralizing all group cash positions, enabling the corporate treasury to:
•Act as the primary banking relationship for subsidiaries
•Provide internal funding and investment services
•Manage foreign exchange and interest rate risks centrally
•Optimize liquidity across the entire organization
Key Components and Functions
1. Cash Pooling and Concentration
Physical Cash Pooling: Actual movement of funds from subsidiary accounts to central accounts, creating a single consolidated cash position.
Notional Cash Pooling: Virtual consolidation where balances remain in local accounts, but interest is calculated on the net position.
Benefits:
•Reduced idle cash balances
•Lower external borrowing needs
•Optimized interest income and expense
2. Payment Factory
A centralized payment processing center that executes all payments on behalf of subsidiaries:
•Standardized payment processes
•Enhanced control and security
•Reduced payment costs
•Improved straight-through processing rates
3. Collection Factory
Centralized receivables management:
•Standardized collection processes
•Accelerated cash collection
•Improved reconciliation
•Enhanced credit management
4. Internal Lending and Borrowing
The IHB acts as an internal lender and borrower:
•Inter-company loans: Providing funding to cash-deficit entities
•Investment services: Managing surplus cash from cash-rich entities
•Transfer pricing: Setting internal interest rates
•Credit risk management: Assessing and managing internal credit exposure
5. Foreign Exchange Management
Centralized FX operations provide:
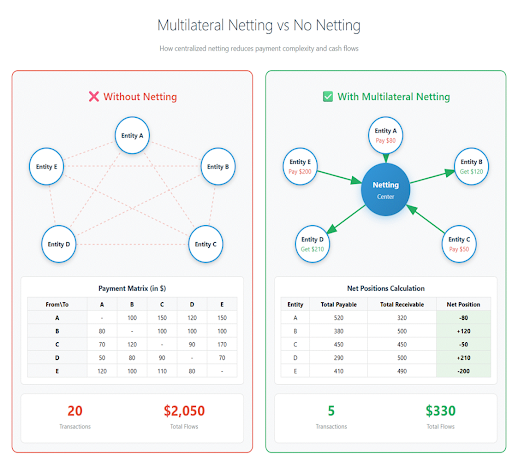
•Netting centers: Offsetting internal FX exposures
•Central FX dealing: Executing all external FX trades
•Risk management: Implementing hedging strategies at group level
•Cost reduction: Minimizing external FX transaction costs
6. Working Capital Optimization
•Supply chain financing: Internal factoring and reverse factoring
•Inventory financing: Funding for subsidiary inventory needs
•Trade finance services: Letters of credit and guarantees
Benefits of In-House Banking
Financial Benefits
Cost Reduction:
•Lower external banking fees
•Reduced transaction costs
•Minimized idle cash balances
•Lower external borrowing costs
Improved Returns:
•Better investment returns on surplus cash
•Optimized interest income through internal lending
•Enhanced yield on overall cash portfolio
Capital Efficiency:
•Reduced working capital requirements
•Improved return on assets
•Better capital allocation across the group
Operational Benefits
Enhanced Control:
•Visibility of cash positions
•Standardized processes and policies
•Improved compliance and risk management
•Better fraud prevention
Process Efficiency:
•Streamlined operations
•Reduced manual interventions
•Faster transaction processing
•Improved reconciliation rates
Strategic Advantages
•Better negotiating power with external banks
•Improved financial flexibility
•Enhanced group-wide liquidity management
•Support for business growth and expansion